Take it for a SPIN! 💫
Version 5.x.x is in a maintenance mode, the new development is ongoing on v6.x.x. Version (v5.x.x) bug fixes will still be available on NPM, if you would like to open a PR for a fix or make a fork, git checkout branch v5.x.x. The new version, v6.0.0 has a multiple improvements (see below) and is not backwards compatible.
Version 6 is a complete rewrite with modern React patterns and architecture. This is a breaking change from v5.x.x.
v6 is now headless - the MultiStep component manages state and logic, but
you control the UI. This gives you complete flexibility over how steps,
navigation, and progress indicators look and behave.
Before (v5): Built-in navigation UI with limited customization
<MultiStep showNavigation activeStep={0} prevButton={...} nextButton={...}>
{/* steps */}
</MultiStep>Now (v6): Bring your own UI, powered by the useMultiStep hook
<MultiStep>
<StepOne title="Personal Info" />
<StepTwo title="Address" />
</MultiStep>;The useMultiStep hook is the core of v6. Any component inside
<MultiStep> can access wizard state and navigation:
import { useMultiStep } from "react-multistep";
function CustomNavigation() {
const {
activeStep, // Current step index (0-based)
stepCount, // Total number of steps
steps, // Array of step metadata
next, // Go to next step
previous, // Go to previous step
goToStep, // Jump to specific step
currentStepValid, // Is current step valid?
} = useMultiStep();
return (
<nav>
<button onClick={previous} disabled={activeStep === 0}>
Back
</button>
<span>Step {activeStep + 1} of {stepCount}</span>
<button onClick={next} disabled={!currentStepValid}>
Next
</button>
</nav>
);
}Key capabilities:
- Access wizard state from any nested component
- Build custom navigation (tabs, progress bars, breadcrumbs)
- Implement complex flows (skip steps, conditional navigation)
- Full TypeScript support
v6 uses React Context internally, eliminating prop drilling:
- Automatic state injection: Every child receives
signalParentcallback - Decoupled architecture: Navigation UI doesn't need to be at the top level
- Flexible composition: Mix and match custom chrome components
Steps control their own validity via the signalParent callback:
function AddressStep({ signalParent }) {
const [zip, setZip] = useState("");
useEffect(() => {
// Signal validity whenever state changes
signalParent({ isValid: zip.length === 5 });
}, [zip, signalParent]);
return <input value={zip} onChange={(e) => setZip(e.target.value)} />;
}Automatic enforcement:
- Next button disabled when
isValid: false - Can't jump forward to invalid steps
- Optional
onValidationErrorcallback
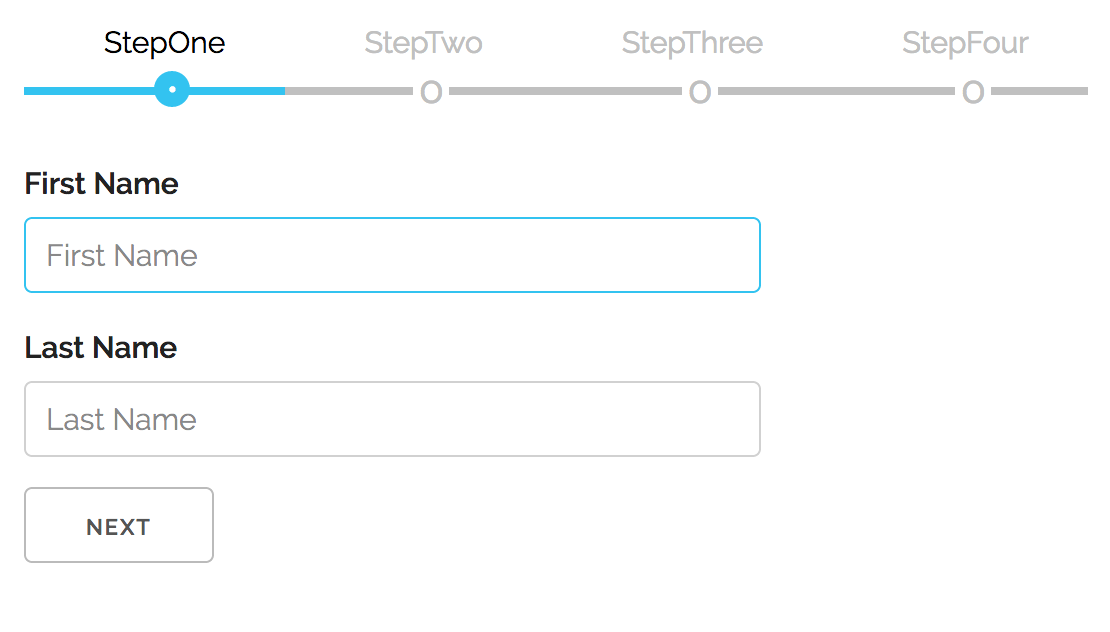
v6 includes an optional modern CSS stylesheet with:
- Mobile-first responsive design (container queries)
- Automatic dark mode (
color-scheme: light dark) - Fluid typography with
clamp() - Touch-optimized tap targets (44px)
- CSS custom properties for easy theming
import "react-multistep/styles"; // Optional!- Core: 10.3kb (logic only)
- CSS: 4.4kb (optional)
- Total: ~15kb vs ~45kb in v5
Removed:
showNavigationpropprevButton/nextButtonprops- Built-in navigation UI
- Style props (
prevStyle,nextStyle, etc.)
Added:
useMultiStephooksignalParentcallback for validation- Context-based architecture
- Optional modern CSS import
- TypeScript-first design
See the example app for a complete working implementation.
v6.1.0 introduces an optional server-side module for building HTMX-powered multi-step wizards with zero client-side JavaScript (except HTMX itself). Perfect for server-rendered applications, progressive enhancement, and when you want the server to control all state and validation.
Key Features:
- ✅ HATEOAS-driven - Server controls which navigation actions are available
- ✅ Light Functional Programming - Pure functions, Result types, ports pattern
- ✅ Zero client-side logic - All state and validation managed server-side
- ✅ HTMX integration - Progressive enhancement with automatic updates
- ✅ Type-safe - Full TypeScript support with branded types
- ✅ Framework-agnostic - Works with any Node.js HTTP framework
- ✅ Session-based - Built-in session store abstraction
The server module is included in the main package:
npm install react-multistepimport {
createWizardHandler,
inMemorySessionStore,
systemClock,
makeStepId,
validationOk,
validationErr,
ok,
} from "react-multistep/server";
import type { WizardConfig, StepDefinition } from "react-multistep/server";
// Define steps with validation and rendering
const steps: StepDefinition[] = [
{
id: makeStepId("personal-info"),
title: "Personal Information",
validate: (data) => {
const d = data as { name?: string; email?: string };
const errors: Record<string, string> = {};
if (!d.name || d.name.length < 2) {
errors.name = "Name must be at least 2 characters";
}
if (!d.email || !d.email.includes("@")) {
errors.email = "Invalid email address";
}
return Object.keys(errors).length > 0
? validationErr(errors)
: validationOk();
},
render: (ctx) => {
const data = ctx.data as { name?: string; email?: string } | null;
const errors = ctx.errors || {};
return ok(`
<fieldset>
<legend>Personal Information</legend>
<input
type="text"
name="name"
value="${data?.name || ""}"
hx-post="/wizard/${ctx.session.id}/update"
hx-trigger="change"
hx-target="#wizard-content"
hx-swap="outerHTML"
/>
${errors.name ? `<span class="error">${errors.name}</span>` : ""}
</fieldset>
`);
},
},
];
// Create wizard configuration
const config: WizardConfig = { steps };
// Create handler with dependency injection
const handler = createWizardHandler(
config,
inMemorySessionStore(),
systemClock(),
{
containerId: 'wizard-shell',
template: ({ containerId, indicators, stepContent, navigation }) => `
<main id="${containerId}">
<aside class="wizard-sidebar">${indicators}</aside>
<section class="wizard-panel">${stepContent}${navigation}</section>
</main>
`,
}
);
// Use with any HTTP framework
app.all("/wizard/*", async (req, res) => {
const response = await handler(req);
res.status(response.status).send(await response.text());
});Pass a fourth renderOptions argument to fully customize the generated HTML:
containerId– override the wrapper element ID (defaultwizard-content)template(ctx)– replace the default layout while reusing rendered piecesrenderNavigation/renderStepIndicators– swap in bespoke markup
Errors are serialized as JSON with sensible HTTP status codes (422 for
validation failures, 404 for missing sessions/steps, 409 for navigation
conflicts, etc.), so clients can react appropriately.
The server module follows Light FP principles with clear separation of concerns:
Pure Core Adapters HTTP
───────────────────── ───────────────────── ────────────────
wizard.ts (pure logic) → session.ts (storage) → http.ts (routes)
renderer.ts (pure HTML) → ports.ts (interfaces) → middleware.ts
types.ts (ADTs)
Pure Functions:
- All domain logic is pure (no I/O, no side effects)
- Validation, rendering, and state transitions are deterministic
- Easy to test and reason about
Result Types:
- All fallible operations return
Result<T, E> - No exceptions in the core - errors are values
- Exhaustive error handling with discriminated unions
Ports Pattern:
- Dependencies injected as interfaces (
SessionStore,Clock,UuidGen) - Easy to swap implementations (in-memory, Redis, database)
- Zero coupling between layers
The wizard handler provides these routes automatically:
GET /wizard/:sessionId- Initialize wizard, render first stepPOST /wizard/:sessionId/update- Update current step data (triggers validation)POST /wizard/:sessionId/next- Navigate to next stepPOST /wizard/:sessionId/previous- Navigate to previous stepPOST /wizard/:sessionId/goto/:index- Jump to specific stepPOST /wizard/:sessionId/submit- Submit final step
The server module generates HTMX-enhanced HTML with automatic state management:
<!-- Server controls button state based on validation -->
<button
type="button"
hx-post="/wizard/session-123/next"
hx-target="#wizard-content"
hx-swap="outerHTML"
class="wizard-button-next"
>
Next
</button>
<!-- Inputs update server on change -->
<input
type="text"
name="email"
hx-post="/wizard/session-123/update"
hx-trigger="change"
hx-target="#wizard-content"
hx-swap="outerHTML"
/>When a field changes, HTMX posts to the server, which validates, updates session state, and returns the entire updated wizard UI. Navigation buttons automatically enable/disable based on validation state.
Built-in session storage with customizable backends:
import { inMemorySessionStore } from "react-multistep/server";
// In-memory (development)
const store = inMemorySessionStore();
// Or implement your own for production:
import type { SessionStore } from "react-multistep/server";
const redisStore: SessionStore = {
get: async (id) => {
/* ... */
},
set: async (id, session) => {
/* ... */
},
delete: async (id) => {
/* ... */
},
};A full working example with Node.js HTTP server is available:
npm run example:server
# Open http://localhost:8000/See examples/server-side/ for:
- Complete step definitions with validation
- HTMX integration patterns
- Custom HTML rendering
- Session management
- Error handling
- 📘 Extended guide: Server example README
The server module supports intelligent step skipping for optional or conditional sections. Users can jump multiple steps ahead if intermediate steps are skippable based on their data or business rules.
Add a canSkip function to any step definition:
{
id: makeStepId("company-details"),
title: "Company Details",
// Skip this step for personal accounts
canSkip: (session) => {
const basicInfo = session.stepData[0] as { accountType?: string };
return basicInfo?.accountType === "personal";
},
validate: (data) => { /* validation logic */ },
render: (ctx) => { /* render logic */ }
}Always Optional:
canSkip: () => true // Step 3 (marketing preferences) always skippableConditional Logic:
canSkip: (session) => {
const userType = session.stepData[0] as { type: string };
return userType?.type === "existing_customer"; // Skip onboarding for existing users
}Complex Business Rules:
canSkip: (session) => {
const userRole = session.metadata.userRole;
const hasCompletedBefore = session.metadata.returning;
return userRole === "admin" || hasCompletedBefore;
}The enhanced navigation logic allows users to jump multiple steps when intermediate steps are skippable:
- Step 1 → Step 4: If Steps 2 & 3 are both skippable
- Step 2 → Step 5: If Steps 3 & 4 can be skipped based on Step 2's data
- Intelligent blocking: Navigation blocked if any required intermediate step is invalid
// Enhanced canGoToStep logic:
if (targetStep > currentStep + 1) {
// Multi-step jump attempt
if (!currentStepValid) return false; // Current step must be valid
// Check all intermediate steps
for (let i = currentStep + 1; i < targetStep; i++) {
const step = config.steps[i];
const canSkip = step?.canSkip?.(session) ?? false;
// Block if step can't be skipped AND isn't already valid
if (!canSkip && !session.stepValidity[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true; // ✅ Jump allowed
}Try the enhanced skip logic with a complete example:
# Run the skip logic demo
node examples/server-side/skip-example.js
# Open http://localhost:8001/Demo flow:
- Choose "Personal" account → Company details (Step 2) becomes skippable
- Choose "Business" account → Company details required
- Marketing preferences (Step 3) always optional
- Jump directly from Step 1 to Step 4 when steps are skippable
Step indicators automatically reflect skip states in the UI:
<!-- Skippable steps show different styling -->
<li class="step-indicator skippable">
<button hx-post="/wizard/session/goto/2">2. Optional Step</button>
</li>
<!-- Required steps block navigation until valid -->
<li class="step-indicator required invalid">
<span>3. Required Step</span> <!-- Not clickable -->
</li>The server controls all navigation logic - HTMX simply enables the interactions that the server determines are valid based on current state and skip rules.
Use Server-Side when:
- You want zero client-side JavaScript (progressive enhancement)
- Server controls all state and business logic
- You need server-side validation and security
- Building forms that work without JavaScript
- Using server-side rendering frameworks (Next.js, Remix, etc.)
Use Client-Side when:
- You want rich interactive UIs
- Need offline capabilities
- Want instant validation feedback
- Building single-page applications
- Client-side state management (Redux, Zustand, etc.)
Both modules can coexist in the same application for different use cases.
To use this module in your app run:
npm install react-multistepnext, import it inside of your app:
import MultiStep from "react-multistep";and then, in your application, you add your custom components/forms this way:
<MultiStep>
<StepOne title="Step 1" />
<StepTwo title="Step 2" />
</MultiStep>;Because v6 is headless, you provide the surrounding chrome yourself. A minimal layout might be:
import { MultiStep, useMultiStep } from "react-multistep";
import type { StepComponentProps } from "react-multistep";
function WizardChrome({ children }: { children: React.ReactNode }) {
const { steps, activeStep, goToStep, next, previous, currentStepValid } =
useMultiStep();
return (
<div>
<ol role="tablist" aria-label="Wizard steps">
{steps.map((step) => (
<li key={step.index}>
<button
role="tab"
aria-selected={step.index === activeStep}
onClick={() => goToStep(step.index)}
>
{step.title ?? `Step ${step.index + 1}`}
</button>
</li>
))}
</ol>
<div role="tabpanel">{children}</div>
<div>
<button onClick={previous} disabled={activeStep === 0}>Prev</button>
{activeStep < steps.length - 1 && (
<button onClick={next} disabled={!currentStepValid}>Next</button>
)}
</div>
</div>
);
}
function StepOne({ signalParent }: StepComponentProps) {
const [value, setValue] = useState("");
useEffect(() => {
signalParent({ isValid: value.trim().length > 0 });
}, [value, signalParent]);
return (
<WizardChrome>
<input value={value} onChange={(event) => setValue(event.target.value)} />
</WizardChrome>
);
}| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
children |
React.ReactNode |
– | Steps to render. Each child is cloned and receives a signalParent prop. |
activeStep |
number |
uncontrolled | Controls the active step index. Leave undefined for internal state. |
initialStep |
number |
0 |
Starting step when using internal state. |
onStepChange |
(step: number) => void |
undefined |
Fires whenever the active step changes (manual or programmatic). |
onValidationError |
(activeStep: number) => void |
undefined |
Called when the user tries to advance while the current step is invalid. |
Each child receives a signalParent callback used to report validation state:
props.signalParent({ isValid: boolean, goto?: number });If isValid is false, the Next button is disabled and step jumping forward is
blocked. The optional goto field lets you hint which step the wizard should
focus when navigation fails. When the user tries to advance past an invalid
step, MultiStep will attempt to redirect to goto (clamped to the available
steps) if that target is already valid—handy for summary/review screens that
need to bounce the user back to the first incomplete section.
TypeScript tip: extend the provided
StepComponentPropstype to get full autocomplete forsignalParentand the optionaltitleprop:import type { StepComponentProps } from "react-multistep"; type AccountStepProps = StepComponentProps<{ plan: Plan }>
Any descendant of MultiStep can tap into a hook family to inspect navigation
state or drive custom controls:
import { useMultiStepState, useStepNavigation } from "react-multistep";
function WizardChrome({ children }: React.PropsWithChildren) {
const { steps, activeStep, currentStepValid, stepCount } = useMultiStepState();
const { previous, next, goToStep } = useStepNavigation();
return (
<div>
<p>{`Step ${activeStep + 1} of ${stepCount}`}</p>
<ol role="tablist">
{steps.map((step) => (
<li key={step.index}>
<button onClick={() => goToStep(step.index)}>{step.title}</button>
</li>
))}
</ol>
<div role="tabpanel">{children}</div>
<button onClick={previous} disabled={activeStep === 0}>Prev</button>
<button onClick={next} disabled={!currentStepValid}>Next</button>
</div>
);
}Returns the full context object for cases where you need everything at once. The shape matches the bullet list below.
Prefer these slice hooks for most real-world UIs—they only trigger re-renders when the specific slice changes, which keeps custom chrome components snappy.
Convenience helper that just gives you steps (useful for read-only indicators
or analytics).
All hooks share the same data model:
activeStep: current index (0-based)stepCount: total number of registered stepssteps: array describing each step{ index, isActive, isValid, title }goToStep(step): programmatically navigate to any step (respects validation rules)next()/previous(): shortcuts for relative navigationsetStepValidity(index, isValid): manually toggle a step’s validity (exposed viauseMultiStep()anduseStepNavigation()for async workflows)isStepValid(index): read cached validity for any stepcurrentStepValid: convenience boolean for the active step
When the child form component needs to control the Next button, call
signalParent inside your component whenever validity changes:
useEffect(() => {
props.signalParent({ isValid: formIsValid });
}, [formIsValid, props.signalParent]);The example app demonstrates a reusable chrome component that consumes the hook and renders the navigation UI for each step.
Version 6.0.0 includes an optional modern CSS stylesheet with mobile-first, responsive design:
// Import the optional stylesheet
import "react-multistep/styles";Features:
- Mobile-first responsive design with container queries
- Automatic dark mode support via
color-scheme: light dark - Fluid typography using
clamp()for adaptive sizing - Touch-optimized tap targets (44px minimum)
- CSS custom properties for easy theming
- Modern CSS features:
@layer,light-dark(), logical properties - Backward compatible: Works without the CSS, enhanced with it
Customization:
All styles use CSS custom properties with sensible defaults:
:root {
--multistep-primary: #1eaedb;
--multistep-inactive: silver;
--multistep-bg: #f1f1f141;
--multistep-spacing-md: clamp(2rem, 3vw, 4rem);
--multistep-button-size: clamp(2.5rem, 5vw, 4rem);
/* ...and more */
}Override any variable in your own CSS to customize colors, spacing, or typography. The component adapts automatically to small screens (mobile) and large screens (desktop) without media queries using container queries.
Start by cloning the repo locally:
git clone https://github.com/srdjan/react-multistep.gitthen:
cd react-multistep // (1) navigate to the project folder
npm install // (2) install dependencies
npm run build // (3) build the componentOn a successful build, try the example app:
cd ./examples/client-side // (1) navigate to the example folder
npm install // (2) install dependencies
npm run dev // (3) build the library + run esbuild dev server (http://localhost:8000)
# optional
npm run build // production bundle to ./distNow, you can open the example in your favorite browser...