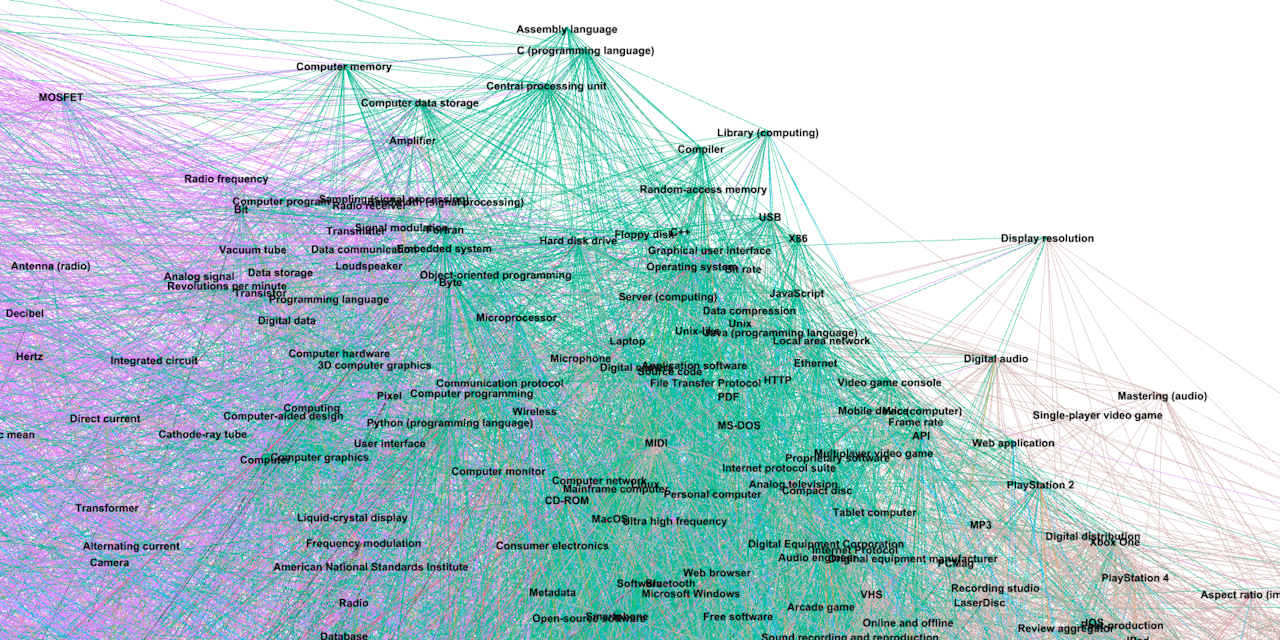
A parser and analyzer for Wikipedia database dumps, written in Rust.
- Generate the graph linking each article to its sources (= parents)
- Find the shortest path between 2 Wikipedia articles using the BFS algorithm
- Keep the most important vertexes using algorithms such as the PageRank algorithm
- Render the graph using Gephi
# Clone the repository:
git clone git@github.com:rreemmii-dev/Wikipedia-Database-Parser-Analyzer.git
cd Wikipedia-Database-Parser-AnalyzerEnsure you have cargo installed.
- Download a Wikipedia dump. A list can be found here, and a download tutorial here. The latest dump I used is English Wikipedia, 2025-06-01 (uncompressed size of 103 GB, contains more than 7 million parsed articles).
- Extract the dump.
- Set the
WIKI_PATHconstant in both src/main.rs and src/simple_main.rs to the dump file path, relative toCargo.toml.
src/simple_main.rs does the following:
- Generates required databases and saves them in files (using
generate_databases, see #Provided tools/Generate and load link databases for more information). - Loads databases from generated files.
- Executes a BFS to find the shortest path from the
Wikipediaarticle to theRust_(programming_language)article. - Filters the graph to keep only vertexes having more than 1000 children or parents.
- Exports the filtered graph as a CSV file.
It can be run using:
cargo run --release --bin ExampleRun the src/main.rs file
cargo run --releasegenerate_databases in src/database/generate_database.rs generates the following databases:
graph: The graph with each article pointing towards its sources, stored as an adjacency list. Each article is represented by an ID.name_from_id: The article name corresponding to the article ID.
Databases are saved in files, so you can run generate_databases once and for all.
load_graph and load_name_from_id_and_id_from_name in src/database/load_database.rs load the two previous databases, plus the id_from_name database.
There are 2 graph types, both being adjacency lists:
VecGraph(Vec<Vec<usize>>) for computation on the whole graph. See src/graph_utils/vec_graph_utils.rs.HashmapGraph(HashMap<u32, HashSet<u32>>) if some vertexes were to be removed from the graph. See src/graph_utils/hashmap_graph_utils.rs.
The reason for having 2 graph types is that access to Vec elements is much faster than access to HashMap elements, but items cannot be removed from a Vec while leaving other indexes unchanged.
To open the graph in Gephi, it has to be exported as a CSV file using export_as_csv in src/graph_utils/hashmap_graph_utils.rs.
It is then stored as an adjacency list. It is advised to use # as the CSV delimiter (Wikipedia article names cannot contain #).
It is not recommended to export graph having more than 10,000 vertexes. See https://gephi.org/users/requirements/.
Here is some documentation about Wikipedia articles:
- Links parsing:
[[PageName]]links: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Help:Link#Wikilinks_(internal_links){{section link|PageName}}links: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Help:Link#Section_linking_(anchors) and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Section_link{{multi-section link|PageName}}links: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Multi-section_link<nowiki>tag: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Help:Wikitext#Nowiki<syntaxhighlight>tag: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Syntaxhighlight
- Article names:
- Namespaces (e.g.: article names such as "Category:XXX", or "Help:XXX"): https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Namespace
- Name Restrictions: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Naming_conventions_(technical_restrictions) and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Page_name#Technical_restrictions_and_limitations
- Appendice and footnote sections: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Manual_of_Style/Layout#Standard_appendices_and_footers and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Help:Footnotes
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE.md