twin4build: A python package for Data-driven and Ontology-based modeling and simulation of buildings
Dynamic modeling and simulation of buildings, featuring fully differentiable models for parameter estimation and optimal control. Supports integration of semantic models for automatic model generation and fast implementation.
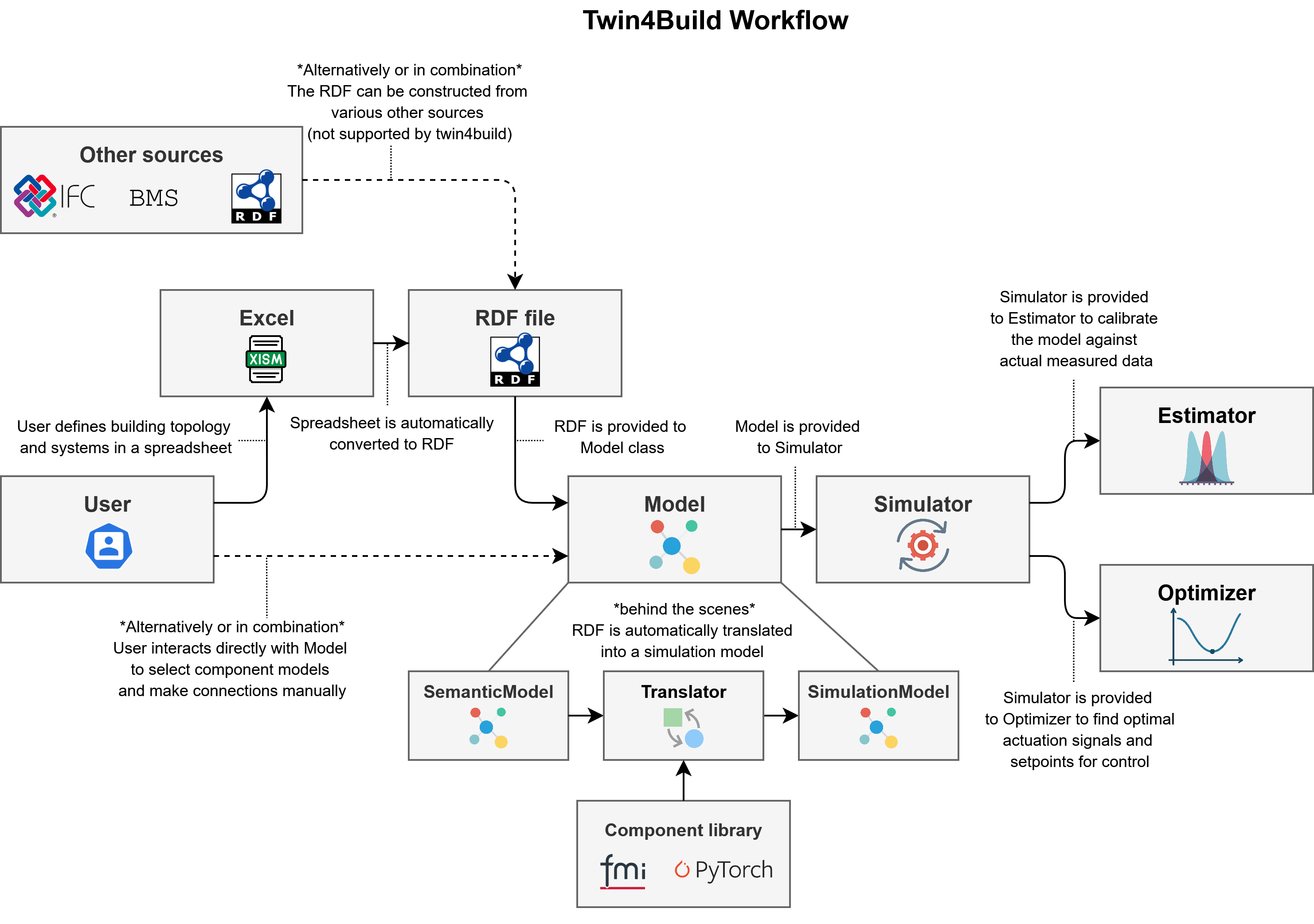
Twin4Build provides several top-level classes for building, simulating, translating, calibrating, and optimizing building energy models:
-
Model:
The main container for your building system, components, and their connections. Use this class to assemble your digital twin from reusable components. -
Simulator:
Runs time-based simulations of your Model, producing time series outputs for all components. Handles the simulation loop and time stepping. -
Translator:
Automatically generates a Model from a semantic model (ontology-based building description) and maintains a link between these. Enables ontology-driven, automated model creation. -
Estimator:
Performs parameter estimation (calibration) for your Model using measured data. Supports both least-squares and PyTorch-based optimization. -
Optimizer:
Optimizes building operation by adjusting setpoints or control variables to minimize objectives or satisfy constraints, using gradient-based methods.
All classes are accessible via the main package import:
import twin4build as tbA typical workflow would look like this:
Below are some examples of how to use the package. More examples are coming soon.
-
Part 1: Connecting components, simulating a model, and visualization
-
Part 2: Modeling and control of indoor CO2 concentration
-
Part 1: Optimization of space heater power consumption, constrained by heating and cooling setpoints.
The documentation can be found online. Below is a code snippet showing the basic functionality of the package.
import twin4build as tb
# Create a model
model = tb.Model(id="example_model")
# Define components
damper = tb.DamperTorchSystem(id="damper")
space = tb.BuildingSpaceTorchSystem("space")
# Add connections to the model
self.add_connection(damper, space,
"airFlowRate", "supplyAirFlowRate")
# Load the model
model.load()
# Create a simulator instance
simulator = tb.Simulator(model)
# Simulate the model
step_size = 600 #Seconds
start_time = datetime.datetime(year=2025, month=1, day=10, hour=0, minute=0, second=0) # Optionally set the timezone
end_time = datetime.datetime(year=2025, month=1, day=12, hour=0, minute=0, second=0) # Optionally set the timezone
simulator.simulate(step_size=step_size,
start_time=start_time,
end_time=end_time)
# Plot the results
plot.plot_component(simulator,
components_1axis=[("Damper", "airFlowRate")],
components_2axis=[("Damper", "damperPosition")],
ylabel_1axis="Air flow rate", #Optional
ylabel_2axis="Damper position", #Optional
show=True,
nticks=11)The package is installed with pip:
pip install twin4buildThe following python versions are supported:
| Python version | Windows | Ubuntu |
|---|---|---|
| 3.9 | ||
| 3.10 | ||
| 3.11 | ||
| 3.12 |
To utilize the graph-drawing capabilities of twin4build, the drawing engine Graphviz must be installed. It can be installed by downloading the install-file from the official website or by using your favorite package manager:
sudo add-apt-repository universe
sudo apt update
sudo apt install graphvizOn windows, the winget or choco package managers can be used:
winget install graphvizchoco install graphvizbrew install graphviz[1] Bjørnskov, J. & Thomsen, A. & Jradi, M. (2025). Large-scale field demonstration of an interoperable and ontology-based energy modeling framework for building digital twins. Applied Energy, 387, [125597]
[2] Bjørnskov, J. & Jradi, M. & Wetter, M. (2025). Automated Model Generation and Parameter Estimation of Building Energy Models Using an Ontology-Based Framework. Energy and Buildings 329, [115228]
[3] Bjørnskov, J. & Jradi, M. (2023). An Ontology-Based Innovative Energy Modeling Framework for Scalable and Adaptable Building Digital Twins. Energy and Buildings, 292, [113146].
[4] Bjørnskov, J., Badhwar, A., Singh, D., Sehgal, M., Åkesson, R., & Jradi, M. (2025). Development and demonstration of a digital twin platform leveraging ontologies and data-driven simulation models. Journal of Building Performance Simulation, 1–13.
[5] Bjørnskov, J. & Jradi, M. (2023). Implementation and demonstration of an automated energy modeling framework for scalable and adaptable building digital twins based on the SAREF ontology. Building Simulation.
[6] Andersen, A. H. & Bjørnskov, J. & Jradi, M. (2023). Adaptable and Scalable Energy Modeling of Ventilation Systems as Part of Building Digital Twins. In Proceedings of the 18th International IBPSA Building Simulation Conference: BS2023 International Building Performance Simulation Association.
@article{OntologyBasedBuildingModelingFramework,
title = {An ontology-based innovative energy modeling framework for scalable and adaptable building digital twins},
journal = {Energy and Buildings},
volume = {292},
pages = {113146},
year = {2023},
issn = {0378-7788},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2023.113146},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378778823003766},
author = {Jakob Bjørnskov and Muhyiddine Jradi},
keywords = {Digital twin, Data-driven, Building energy model, Building simulation, Ontology, SAREF},
}